Have you ever stopped to consider the unseen forces that keep your body functioning? Just as the foundations of a home provide strength and stability, essential minerals play a pivotal role in supporting our health. Among them is a mineral often overlooked in favor of calcium—yet equally vital for our well-being. Comprising about 1% of our total body weight, this nutrient supports everything from strong bones to sustained energy levels. Exploring its role isn’t just about understanding nutrition; it’s about uncovering a key to vitality and balance.
As you read on, you’ll learn about its wide-ranging benefits, the best dietary sources, and the daily requirements needed to maintain optimal health and well-being.
Key Takeaways
- Phosphorus makes up about 1% to 1.4% of the fat-free mass in the human body.
- 85% of phosphorus is found in bones and teeth, highlighting its importance for bone health.
- Animal sources provide a higher absorption rate of phosphorus compared to plant sources.
- Common dietary sources include dairy products, bakery items, vegetables, and chicken.
- The Recommended Dietary Allowance for adults is set at 700 mg per day.
- Phosphorus deficiency is rare due to its availability in various food sources.
- Excessive phosphorus intake can be harmful, particularly in individuals with kidney disease.
Introduction to Phosphorus
Understanding this vital mineral is key to recognizing its critical role in overall health. Representing about 1% to 1.4% of the body’s fat-free mass, it is primarily stored in bones and teeth, with approximately 85% dedicated to structural functions. Beyond this, it is also found in blood and soft tissues, highlighting its widespread importance in various biological processes.
What is Phosphorus?
This essential mineral performs numerous vital functions in the body. As a key component of DNA and RNA, it plays a foundational role in cellular processes. It is also integral to energy production, forming part of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the molecule responsible for energy transfer within cells. Additionally, it activates various enzymes, helps maintain normal pH levels, and supports crucial physiological processes such as muscle contraction and maintaining a regular heartbeat.
Importance of Phosphorus in the Body
This essential mineral plays a critical role in building strong bones and facilitating tissue repair. It supports kidney function by aiding in waste filtration and ensures the proper utilization of key nutrients like vitamins B and D, as well as magnesium and zinc. However, the typical Western diet often provides more of this mineral than calcium, potentially compromising bone health. Striking a balance between these two nutrients is vital for preventing conditions such as osteoporosis, particularly in higher-risk groups like women. Understanding the relationship between this nutrient and health underscores the importance of adequate intake while avoiding excess, which could lead to complications such as cardiovascular issues.
Phosphorus: Health Benefits, Sources, and Daily Requirements
Phosphorus plays a significant role in various biological processes, contributing to overall health. Understanding how this essential mineral benefits the body can help in making informed dietary choices.
Role in Bone Health
Phosphorus is vital for maintaining strong bones and teeth. It works closely with calcium to form hydroxyapatite, the primary mineral component, ensuring optimal bone density. A balanced intake of phosphorus and calcium is essential; a high phosphorus diet without adequate calcium may lead to increased serum parathyroid hormone levels, which can negatively affect phosphorus for bone health.
Contribution to Energy Production
This mineral is a key component of ATP, which serves as the primary energy carrier within cells. Efficient phosphorus and energy production is crucial for converting carbohydrates and fats into usable energy. This conversion supports muscle contractions and enhances overall physiological performance during both exercise and daily activities.
Involvement in Tissue Growth and Repair
Phosphorus plays a fundamental role in tissue growth and repair. It aids in protein synthesis and supports cellular function by being integral to DNA and RNA formation. These processes are essential for cell reproduction and repair, highlighting the importance of phosphorus for tissue repair in maintaining health and vitality.
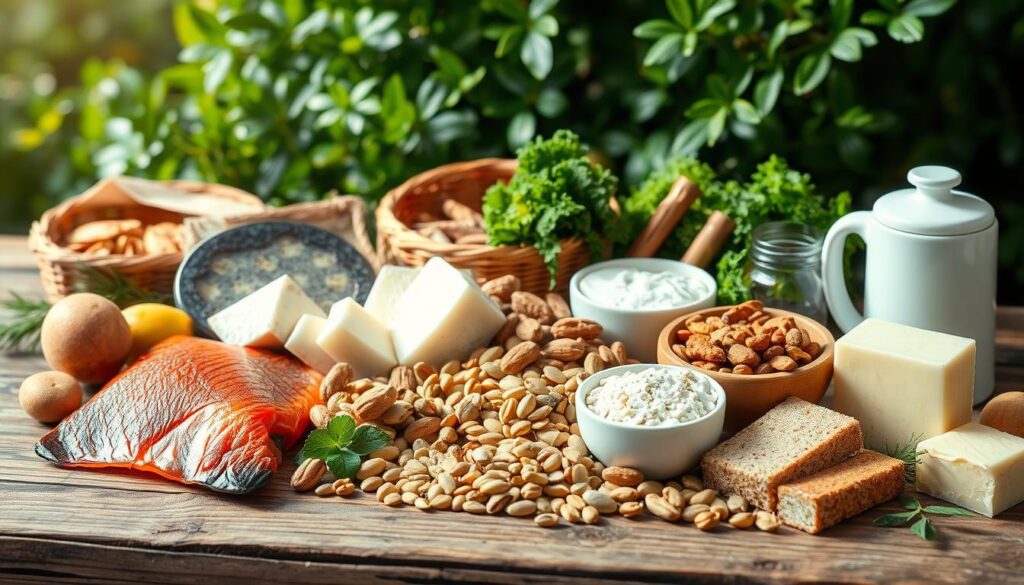
Sources of Phosphorus
Phosphorus is abundant in many foods, making it accessible for those aiming to maintain adequate phosphorus intake. Understanding the various sources can help individuals optimize their diets, ensuring they’re consuming sufficient amounts of this essential mineral.
Phosphorus-Rich Foods
Many phosphorus-rich foods are found in everyday diets, particularly among protein-rich options. Meat, poultry, and fish are excellent examples, with chicken and turkey providing approximately 194-196 mg of phosphorus per 3-ounce serving, covering nearly 16% of the Daily Value (DV). Dairy products also contribute notably; for instance, skim milk and Romano cheese offer 17%-21% of the DV per serving. Legumes like beans and lentils can deliver at least 250 mg per cup, serving up over 28% of the DV. Whole grains, particularly spelt and oats, present varying levels of phosphorus too, typically between 8%-23% per cooked cup.
Phosphorus in Dietary Supplements
For those who may struggle to meet their daily phosphorus needs through diet alone, phosphorus supplements provide a viable alternative. Typically available as standalone products or included in multivitamins, these supplements are often composed of phosphate salts, boasting absorption rates of around 70%. This makes them an effective option for individuals looking to increase their phosphorus intake efficiently. While most adults can achieve adequate levels through well-rounded diets, supplements remain a practical choice for specific needs.
Processed Foods and Additives
Many processed foods phosphorus can significantly impact overall phosphorus intake. Common items such as fast foods, deli meats, and canned beverages often contain phosphorus additives, which contribute around 155 mg of phosphorus per day and account for as much as 30% of phosphorus consumption in the U.S. diet. While these forms of phosphorus are easily absorbed, high intake of processed foods can lead to imbalances and potential health issues. Understanding the role of phosphorus additives in food products helps individuals better assess their dietary choices and manage their phosphorus levels effectively.
Daily Phosphorus Requirements
Understanding daily phosphorus needs is essential for maintaining overall health. Each individual has distinct phosphorus requirements based on their age and gender. The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for phosphorus serves as a guideline for optimal intake, helping people meet their daily phosphorus needs effectively.
Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA)
The phosphorus RDA for adults, both men and women aged 19 years and older, is set at 700 mg per day. This amount ensures that adults receive sufficient phosphorus to support various bodily functions, including bone health and energy production. For children ages 9 to 18, the requirement significantly increases to 1,250 mg daily, reflecting their growth and development needs. Infants and younger children have an established Adequate Intake (AI) level that accommodates their lower phosphorus needs.
Age and Gender Variations
Phosphorus needs by age and gender vary, emphasizing the nutrient’s role at different life stages. Pregnant and lactating women require increased phosphorus amounts, aligning with their physiological demands. For instance, their phosphorus intake by gender is crucial as it influences both maternal health and fetal development. Additionally, the tolerable upper intake levels (UL) suggest that for adults aged 19 to 70, 4,000 mg of phosphorus daily is the maximum safe intake. For individuals over 71 years, the UL is 3,000 mg. Awareness of these guidelines helps prevent potential phosphorus toxicity while ensuring adequate nutrition.
Phosphorus Deficiency and Toxicity
Maintaining balanced levels of this vital mineral is essential for overall health. While deficiencies are uncommon, certain factors can lead to low levels in the body. Nutritional imbalances, specific medications, chronic alcoholism, and conditions that impair nutrient absorption are common contributors. Those at risk should pay close attention to their dietary intake to ensure their needs are met.
Causes of Phosphorus Deficiency
Several factors can lead to phosphorus deficiency. Poor dietary choices, malnutrition, and specific medical conditions can hinder the body’s ability to absorb phosphorus, causing low phosphorus levels. Conditions like diabetes or chronic kidney disease may further complicate regulation of phosphorus in the body. Additionally, some medications may interfere with phosphorus absorption, contributing to symptoms of phosphorus deficiency.
Symptoms and Health Implications
Recognizing the symptoms of phosphorus deficiency is vital for early intervention. Signs include joint pain, fatigue, irritability, and impaired bone development, particularly in children. These health effects of low phosphorus can severely impact daily life and require immediate dietary adjustments to restore normal levels. A well-rounded diet rich in natural phosphorus sources can prevent adverse health outcomes associated with deficiency.
Risks of Excessive Phosphorus Intake
While insufficient levels of this mineral pose health risks, excessive amounts in the blood, a condition known as hyperphosphatemia, can also lead to serious complications. Overconsumption, often stemming from processed foods and supplements, may cause mineral deposits in soft tissues and disrupt the body’s calcium balance. These issues are particularly concerning for individuals with impaired kidney function, who are at a higher risk of toxicity. Monitoring dietary intake is crucial to prevent such complications and maintain overall health.
Conclusion
In summary, this essential mineral plays a vital role in maintaining health by supporting energy production, bone strength, and tissue repair. Recognizing its importance for overall well-being is crucial for making informed dietary choices. While the recommended daily intake for adults varies, many individuals following Western diets often exceed these requirements, underscoring the need for awareness regarding consumption levels.
Adequate intake ensures the body can efficiently perform vital functions. Most foods, especially protein-rich ones, provide sufficient amounts, but it’s essential to monitor dietary sources to avoid risks associated with both deficiencies and excessive intake. A balanced diet remains the cornerstone of achieving optimal levels and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Ultimately, staying informed about the benefits of this nutrient and understanding how to source it effectively can significantly enhance health outcomes across all life stages. A thoughtful approach to nutrition helps prevent deficiencies and mitigates the risks of consuming unnecessarily high amounts, promoting long-term well-being.









